
Foresight
- 16 Oct 23
-
 2134
2134
-
What, Suddenly Hacked! How Will Companies Respond to Cyber Criminals Adapting to the Digital World?
Key Takeaways:
- Cybersecurity poses a significant challenge in the digital era. Currently, even non-professionals adapt and seek opportunities from various vulnerabilities that arise due to the continuous development and emergence of new technologies.
- The problems that arise, including future trends in Cybersecurity, remain concerning. These trends involve the growing accessibility of data and platforms that are widespread and customizable for various purposes. The utilization of AI, machine learning, and other technologies contributes to increasingly sophisticated attack patterns. The evolving regulatory landscape also poses challenges, and the issue of the ongoing shortage of knowledgeable and skilled personnel persists.
- The year 2030 will bring about numerous new challenges in terms of cyber threats. Organizational leaders must not only invest in future technologies but also invest in Cybersecurity for the future.
Cyber-attacks come in various forms, occur constantly, and are widespread across the globe.
Real-time examples can be observed here. Presently, due to the rapid development and emergence of new technologies, the cyber threat landscape continues to expand, providing cybercriminals with more opportunities for attacks. With the ongoing evolution of technology, cybercriminals adapt and leverage the benefits of continuously advancing technology to exploit vulnerabilities in the online world.
"Data" is considered a highly valuable asset, especially personal data and confidential business information, both of which are frequent targets of cyber-attacks. It's evident that in this highly advanced technological era, opportunities abound, but they come hand-in-hand with the challenge of maintaining cybersecurity.
Cybersecurity, an ongoing battle with out end
.jpg.aspx)
Image by Freepik
In Thailand, Kaspersky, a globally recognized cybersecurity service provider, recently revealed that in 2022, they detected more than 17 million instances of threats from various websites targeting users in Thailand. Additionally, the country is facing an increase in cybercrimes in the financial sector. There have been reports and complaints filed through the website of the Royal Thai Police, totaling up to 163,091 cases, resulting in approximately 27.3 billion Thai Baht in damages.
On a global scale, McKinsey, a leading global consulting firm, predicts that by 2025, the Cybersecurity market will witness expenditures reaching up to $101.5 billion. Costs related to cybersecurity-related crimes are estimated to increase by around 15% annually, projecting expenses of up to $10.5 trillion per year. These indicators highlight the growing concerns and continuous rise of cyberattacks in the digital landscape.
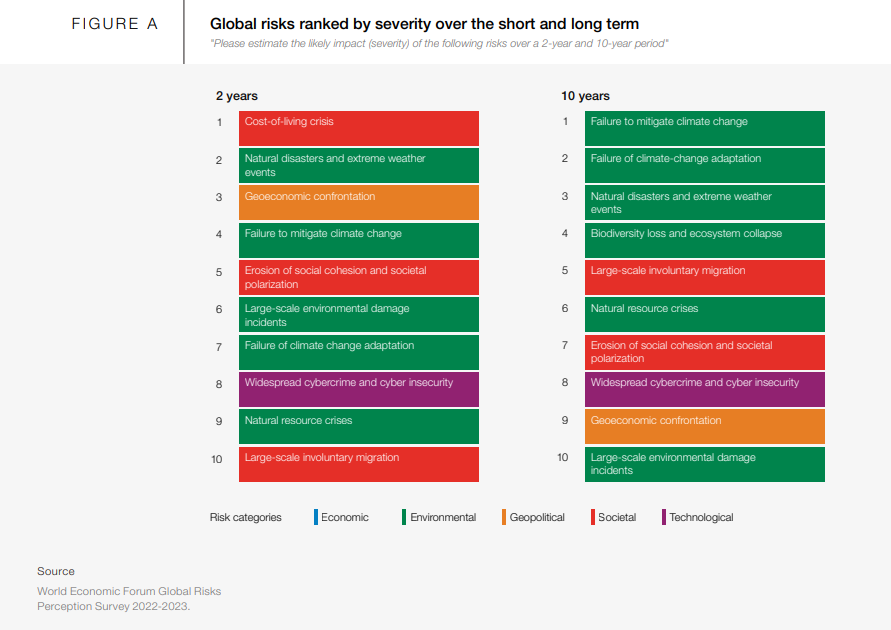
Image by World Economic Forum
The Global Risk Report 2023 by the World Economic Forum ranks various global risks based on their severity level, both in 2025 and 2030. Interestingly, the only issue that falls within the top 10 global risks with the highest severity level related to technology is the topic of cybersecurity. This issue is named "Widespread Cybercrime and Cyber Insecurity," and it is considered highly challenging and persistent. Consequently, organizations need to be well-prepared to address this issue, looking at it from a long-term perspective.
Moreover, McKinsey has highlighted that the growing on-demand access to ubiquitous data and information platforms is leading to an increased likelihood of breaches. The web hosting service market is expected to generate revenues of around $183.18 billion by 2026. Furthermore, in 2020, an average of 1.7 megabytes of data was generated per person per second, emphasizing the importance of cloud systems. This accumulation of data allows organizations to gather more customer-related information for a better understanding of behavior and improved predictive capabilities. This also requires organizations to increase their responsibilities in terms of data storage, management, and protection, as the challenge of handling vast amounts of data will continue to rise in the future."
Cybercriminals are utilizing AI, machine learning, and other advanced technologies to perpetrate increasingly sophisticated attacks. They are evolving into complex, modernized entities employing advanced tools such as AI, machine learning, and automated systems for cyberattacks. Extensive research and development (R&D) in this field have expanded the scope of potential threats, making it even more challenging to defend against them. Furthermore, these cybercriminals are likely to reduce attack durations from weeks to days or even hours in the future, presenting a substantial challenge for organizations across sectors, be it government, private, or national level, to combat such threats. Even if organizations currently possess robust cybersecurity systems, they might become outdated sooner than expected if they don't accelerate their learning and development of cybersecurity to keep up with or surpass the continuous advancements made by cybercriminals.
The ever-growing regulatory landscape and ongoing gaps in, as well as the persistent shortage of skilled and knowledgeable cybersecurity personnel, pose significant challenges. Many organizations still lack a sufficient number of cybersecurity professionals, and this shortage is becoming more pronounced. Furthermore, a considerable number of organizations struggle to identify and address digital risks effectively. Regulatory bodies are now giving cybersecurity greater priority compared to other critical risks, including financial risks like credit risk, and operational and physical safety risks in vital infrastructure.
What will the future of cybersecurity threats look like in 2030?
The world as we know it is transitioning into a Smart World, with the application of AI making everyday devices more intelligent. The interaction between the virtual and physical worlds is becoming more seamless.
Gartner has compiled the 2023 Impact Radar, predicting the emergence of various technologies and trends, considering their impact and the timeline for widespread adoption. It is forecasted that within the next 1-3 years (2024-2026), Multimodal UI will emerge, enabling users and machines to interact in multiple ways simultaneously, such as through speech, gaze, touch, and gestures. This interaction will be facilitated by Digital Twins, which are virtual models of physical objects created using technologies like AI algorithms, IoT, cloud computing, and more. Multimodal UI is expected to have a high impact, while Digital Twins will have a very high impact.
Moving forward, within the next 3-6 years (2026-2029), the utilization of Smart Spaces is predicted. This involves integrating various technologies into cohesive environments to cater to human needs in various aspects of life and work, ultimately becoming an integral part of life. For example, workspaces with internet connectivity to promote Smart cities and Digital Twins. Smart Spaces are projected to have a very high impact.
In the subsequent 6-8 years (2029-2031), Spatial Computing is expected to play a role. This technology calculates spatial relationships and merges physical and digital objects, including Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and Merged Reality (MR), creating a high level of impact.
Lastly, by the year 2031, the emergence of a Metaverse is predicted. This Metaverse will combine virtual world technologies to create environments mirroring the real world, enabling people to interact and engage through avatars in a 3D graphic format. It will simulate real-life activities and interactions more effectively than current social media platforms. Additionally, Digital Humans (AI avatars) will resemble humans in appearance, skin color, facial features, and behavior. The Metaverse is expected to have a very high impact, while Digital Humans will have a high impact."
Furthermore, the European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA) has also forecasted the top 10 emerging cybersecurity threats that are expected to occur in the year 2030. This is certainly worth paying attention to. Let's take a closer look and examine what types of cyber threats are projected for 2030. It's important for each organization to assess whether they have effectively prepared and are ready to handle these potential threats. Let's explore this further.

1. Supply chain compromise of software dependencies
Using components and services from third-party suppliers and partners in the supply chain may create unexpected risks for both the suppliers themselves and their customers.
2. Advanced disinformation campaigns
The use of advanced techniques like deepfakes, which generate realistic synthetic media, can be exploited by malicious actors for political manipulation, damaging reputations, and economic deception.
3. Rise of digital surveillance authoritarianism/loss of privacy
Facial recognition systems used to track users on digital platforms or the collection of digital identity data may become targets for future criminal activities, reducing personal privacy.
4. Human error and exploited legacy systems within cyber-physical ecosystems
If systems are not updated and personnel lack the necessary skills, knowledge, training, and understanding of digital infrastructure, it may lead to security vulnerabilities and unauthorized access.
5. Targeted attacks enhanced by smart device data
Attackers may exploit data from internet-connected smart devices to orchestrate sophisticated and highly targeted attacks.
6. Lack of analysis and control of space-based infrastructure and objects
Lack of understanding, analysis, and control over critical infrastructure in outer space, which requires collaboration between governments and private sectors, may result in increased risks of attacks and disruptions to the system.
7. Rise of advanced hybrid threats
Offline attacks are merging with online attacks due to the growing use of interconnected smart devices, cloud services, online identity creation, and social media platforms.
8. Skill shortages
Malicious actors will target organizations with the lowest cybersecurity preparedness, exploiting the skills gap in the cybersecurity workforce.
9. Cross-border ICT service providers as a single point of failure
The information and communication technology sector, including transportation systems, power grids, and international service providers, may be vulnerable to threats and could be used as tools in future conflicts.
10. Artificial intelligence abuse
The manipulation and misuse of AI algorithms and training data can lead to the creation of fake content, biased content, creation of fake biometric data, robotics for military purposes, and the introduction of erroneous or compromised data into datasets.
Preparing for Cybersecurity in the Future

Image by Freepik
From the current situation and potential future cyber risks, organizations can reduce cybersecurity risks by utilizing big data for security maintenance. Employing the concept of Zero-Trust Architecture, which emphasizes "Never trust, Always verify," ensures that everything, whether individuals, systems, or devices, is consistently verified, regardless of whether they come from within or outside the organization. Furthermore, law enforcement in cyberspace employs AI, machine learning, and other technologies to release increasingly complex attacks. Organizations should also enhance their use of automated systems to combat more sophisticated cyberattacks powered by AI and advanced technologies. Employing AI and machine learning helps organizations keep up with evolving attack patterns, enabling them to develop automated technical solutions and automated organizational responses to various threats, including designing and establishing paired cybersecurity measures. These strategies should be paired with technology investments and their application to support the constant increases in regulatory checks and resource gaps.
Organizational leaders must provide answers regarding whether their organizations are prepared for the swift digital transformation that will occur in the next 3, 5, and 10 years. Additionally, organizations must have the foresight to understand how present investments in various technologies will impact future cybersecurity in the cyber world.
Considering the above, it is evident that within the next 8 years, the development of the Smart World will remain dynamic. New technologies will emerge, including the utilization of Multimodal UI Digital Twins within 1-3 years, Smart Space within 3-6 years, Spatial Computing Digital Human, and Metaverse within 6-8 years. These technological advancements will have significant impacts. Therefore, apart from seeking business opportunities through technology investments, organizations must be prepared to invest in cybersecurity aspects, including systems, processes, personnel knowledge development, and tracking new cyber threats consistently.
Most importantly, organizations need to comprehend that Cybersecurity not only creates value for the organization but also differentiates it from competitors in the long run. Though investing in Cybersecurity might not yield immediate returns, it is undoubtedly worthwhile, as inadequate management of attacks can lead to not only financial losses but also diminished confidence and reputation, affecting the organization in the long term.